Materialized View in Django
 A “materialized view” is a database object which stores the result of a precalculated database query and makes it easy to refresh this result as needed.(cybertec-postgresql). It is the replica of query data that does not execute in real time and takes a bit more room, but retrieves data more faster. One can schedule refresh of materialized view so that the latest information is not lost.
A “materialized view” is a database object which stores the result of a precalculated database query and makes it easy to refresh this result as needed.(cybertec-postgresql). It is the replica of query data that does not execute in real time and takes a bit more room, but retrieves data more faster. One can schedule refresh of materialized view so that the latest information is not lost.
Prerequisite Required
1. Python
2. Postgres SQL
3. Psycopg2-binary
For this tutorial, I am going to use PostgresSQL. Any relational database could be used instead of Postgres and Psycopg2-binary is required for Python to talk with Postgres database. If you do not have Psycopg2-binary installed, run the command pip install psycopg2-binary.
Step 0. Setup local database (www.postgresql.org)
Download and install postgres on your local computer. Follow the instruction from Postgres SQL official documentation. Setup the Postgres SQL database to the django app.
Step 1. Write a model to create table on database
In models.py of polls app declare a User model as below:
1
2
3
4
class User(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=10)
age = models.PositiveSmallIntegerField()
phone_num = models.CharField(max_length=10)
Now make migration and migrate the model. Run the command below one after another.
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
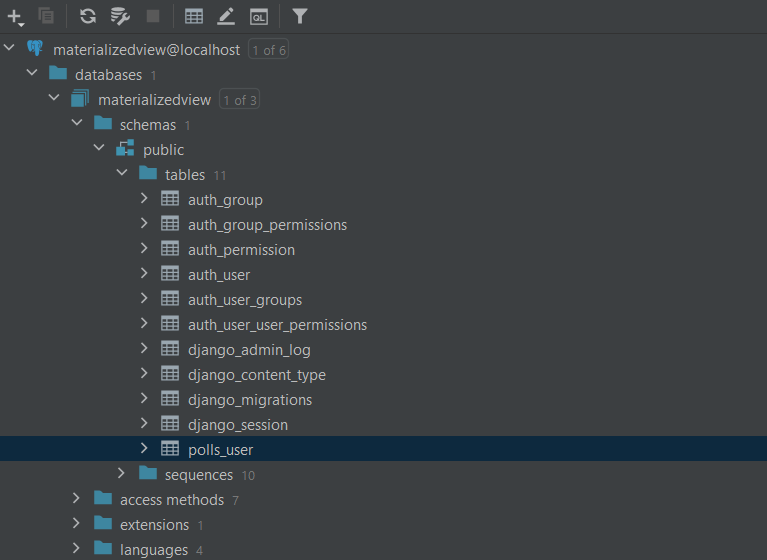
It should create a table polls_user in database. In my case, the name of local database is materializedview and under public schema section, newly migrated table is located.
Now let’s populate some data into the table. I have used a Django admin panel to populate the data.
Step 2. Create a lookup query on original table
Run python shell and execute a query that select all the data from table polls_user.
1
2
3
4
> > > from polls.models import User
> > > count = User.objects.all().count()
> > > print(f"orginal table returns {count} user ")
> > > orginal table returns 5 user
Step 3. Create a materialized view on database
In Postgres SQL, run the following command to generate the materialized view. It generates materialized view with the data where user age is greater or equal to 25.
create materialized view polls_user_matt_view as
SELECT * FROM "polls_user" WHERE "polls_user"."age" >= 25
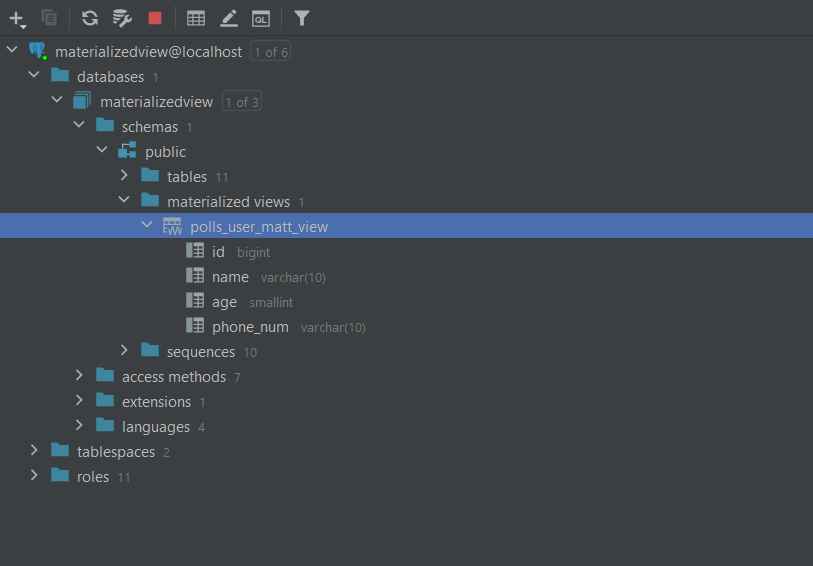
We should be able to see our materialized view which is polls_user_matt_view under Materialized View category.
Step 4. Build a model for materialized view
In models.py of polls app, create a model UserMaterializedView as below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
class UserMaterializedView(models.Model):
name = models.CharField(max_length=10)
age = models.PositiveSmallIntegerField()
phone_num = models.CharField(max_length=10)
class Meta:
managed = False
db_table = 'polls_user_matt_view'
managed = False in model prevents creation of table on original database if the migrations command on polls is executed by mistake in future. The db_table is declared explicitly to allow a Django connection between models and materialized view.
Step 5. Create a lookup query on materialized model
Now create a lookup query on original User model and UserMaterializedView. Run the python console and execute the command below:
1
2
3
4
5
from polls.models import UserMaterializedView, User
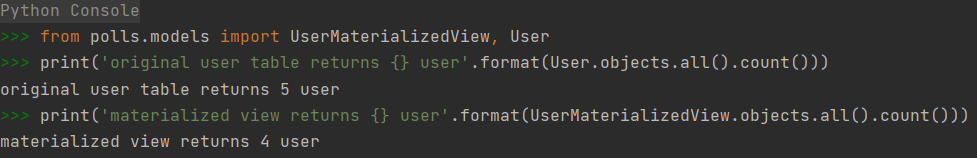
print('original user table returns {} user'.format(User.objects.all().count()))
original user table returns 5 user
print('materialized view returns {} user'.format(UserMaterializedView.objects.all().count()))
materialized view returns 4 user
We should be able to see two prints and materialized view returns less data as expected.




Leave a comment