Reverse Linked List in Python (Iterative Method)

Linked List
A linked list is a linear data structure that includes a series of connected nodes. Here, each node stores the data and the address of the next node. The elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations.
Example 1:
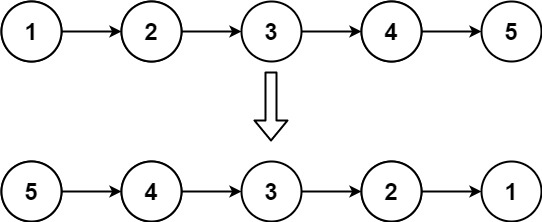
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [5,4,3,2,1]
Example 2:
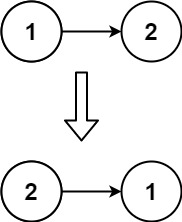
Input: head = [1,2]
Output: [2,1]
Example 3:
Input: head = []
Output: []
Steps to solve the problem:
-
Initialize the two pointers prev and current (Initially point prev to None and current to head of linked list).
prev = None current = head -
Iterate through the linked list in a loop until and unless current is not None and do the following:
a. Declare a temp variable. (It is used to store the next value of current node)
temp = current.nextb. Point next of current to prev.
current.next = prevc. Set prev as current.
prev = currentd. Set current as temp.
current = temp
Code Implementation
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# example input -> 1->2->->3->4->5
def reverseList(head): # prev = None
prev = None # current = 1
current = head
# current = 1 is not None? True
# current = 2 is not None? True
# current = 3 is not None? True
# current = 4 is not None? True
# current = 5 is not None? True
# current = None is not None? False (loop->breaks)
while current is not None:
temp = current.next
#1.next=2, 2.next=3, 3.next=4, 4.next=5, 5.next=None
current.next = prev
#1.next=None, 2.next=1, 3.next=2, 4.next=3, 5.next=4
#None<-1, 1<-2, 2<-3, 3<-4, 4<-5
prev = current
#prev=1, prev=2, prev=3, prev=4, prev=5
current = temp
#current=2, current=3, current=4, current=5,
#current=None
return prev




Leave a comment