Serializer - Django Rest Framework
 Serializer in Django Rest Framework converts complex objects into data types understandable by front-end frameworks. It allows the python native data types to be rendered into JSON, XML, or other content types. Serializer also provides deserialization, which allows the parsed data to be converted back into complex data types only after validating the incoming data.
Serializer in Django Rest Framework converts complex objects into data types understandable by front-end frameworks. It allows the python native data types to be rendered into JSON, XML, or other content types. Serializer also provides deserialization, which allows the parsed data to be converted back into complex data types only after validating the incoming data.
Before moving further, my friend “SB2” wants to meet you and has something to say.

What message did SB2 deliver to you guys? Was it interesting? Was it motivating? What was he trying to say?😕😵 Did you guys respond to him with a message that he could understand? Here, the SB2 is speaking in Sanskrit “प्राता रत्नं प्रातरित्वा दधाति।” which means “An early riser earns good health.”
The same thing goes with the python. It cannot understand the data types of other languages. It needs data in its own native data types to store and understand else it makes no sense to python. Similarly, when python delivers its native and complex data types to other languages, it makes no sense to them as well.
So, what is the solution? Who will save us from the problem?

Now, let’s build a simple API and declare a serializer class.
Model
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
from django.db import models
class Comment(models.Model):
email = models.EmailField()
subject = models.CharField(max_length=250)
created_at = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add=True)
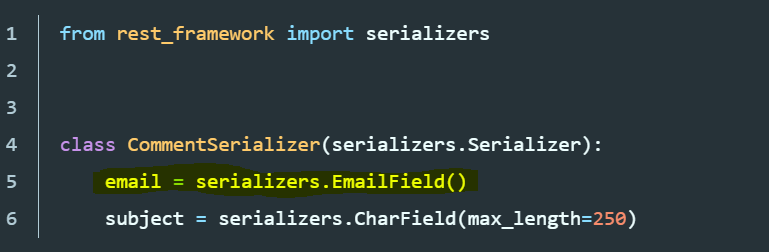
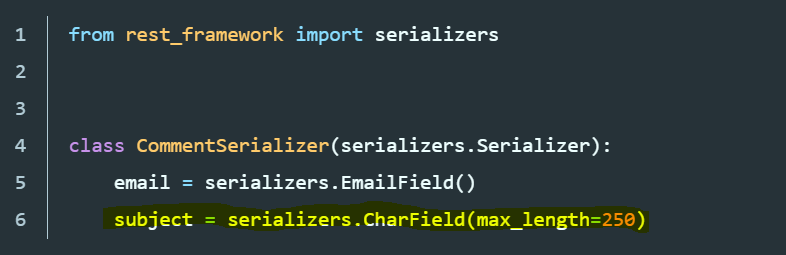
Serializer
1
2
3
4
5
6
from rest_framework import serializers
class CommentSerializer(serializers.Serializer):
email = serializers.EmailField()
subject = serializers.CharField(max_length=250)
View
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
from rest_framework.viewsets import ModelViewSet
from .models import Comment
from .serializer import CommentSerializer
class CommentViewSet(ModelViewSet):
queryset = Comment.objects.all()
serializer_class = CommentSerializer
URL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from app1.views import CommentViewSet
from rest_framework.routers import DefaultRouter
r = DefaultRouter()
r.register('', CommentViewSet, basename='comment')
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
]+r.urls
Let’s add some of the comments using postman. At first, let’s send invalid data.
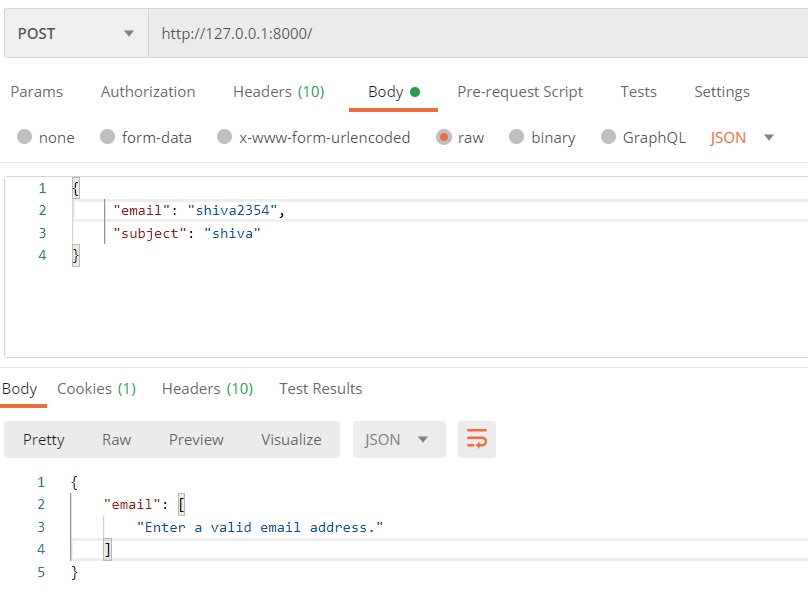
Here, the serializer validates the data before storing it in a database. We have defined in our serializer that the email field should be email, not a character or text.
 So, the serializer validates the incoming data and prevents invalid data from storing into the database.
So, the serializer validates the incoming data and prevents invalid data from storing into the database.
Similarly, let’s add invalid data to the subject and see how our serializer reacts.

In serializer, we have defined that our subject must be no longer than 250 characters.
Therefore serializer is again preventing invalid data and performing validation on every POST request.
NOW, LET’S ADD SOME VALID COMMENTS
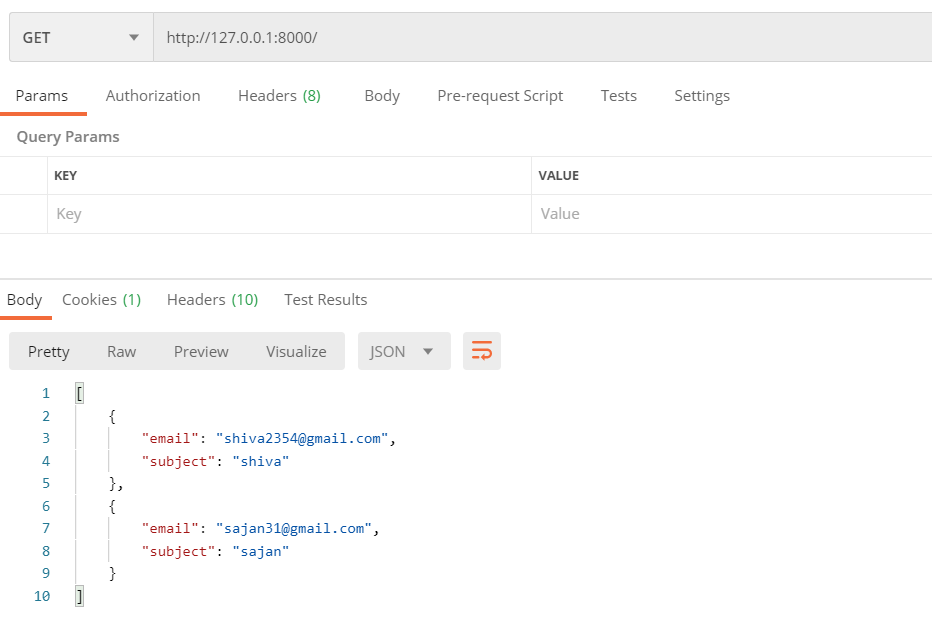 We can see data on GET requests which means that we have added valid data to our database. But as said earlier, python stores data in its native data type, so let’s see if the data is converted into its complex data type or not.
We can see data on GET requests which means that we have added valid data to our database. But as said earlier, python stores data in its native data type, so let’s see if the data is converted into its complex data type or not.
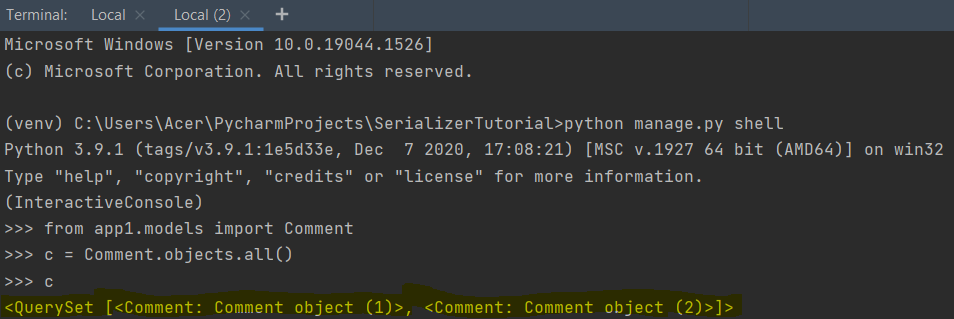
We can see that the comment posted has been deserialized and changed into a QuerySet. QuerySet refers to the list of objects. It is a complex as well as python native data type. The other frontend technologies do not understand such data types, thus the serializer converts such data types into a dictionary and sends them into a format that the front end can understand.




Leave a comment